Self-referential Functionality: A recursive function is distinguished by its ability to call itself, enabling the function to operate on smaller subsets of the problem.
Base Case: This acts as a termination criterion, preventing infinite recursion and ensuring that each recursive call progresses toward this condition.
Bookkeeping Overhead: Recursive calls involve considerable management of function states and return addresses, which can lead to increased memory usage.
/**
* Sums from 1 to n iteratively.
* @param n, positive integer
* @return sum from 1 to n
*/
public static int sum(int n) {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
result = result + i;
}
return result;
}
/**
* Sums from 1 to n recursively.
*
* recSum(5) 15
* 5+recSum(4) 10+5=15
* 4+recSum(3) 6+4=10
* 3+recSum(2) 3+3=6
* 2+recSum(1) = 1+2=3
* @param n
* @return sum from 1 to n
*/
public static int recSum(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return n; // base case
}
return n + recSum(n - 1); // recursive case
}
/**
* Finds n-th fibonacci number.
* @param n, positive value or 0
* @return n-th fibonacci number
*/
public static long fib(int n) {
if (n == 0 || n == 1) {
return n;
}
return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
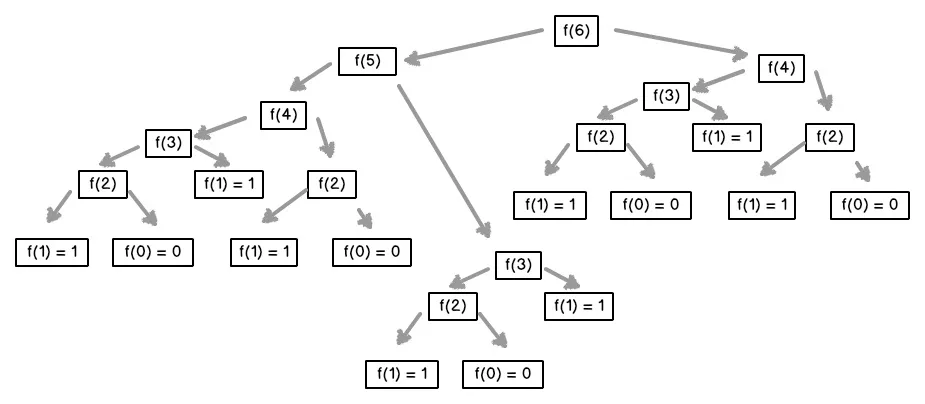
Recursion Tree for fib(6):

/**
* Binary search in a non-null array.
* @param data, int array to search against (ordered in ascending order)
* @param key, int key value to search for
* @return index if found, -1 if not found
*/
public static int find(int[] data, int key) {
return find(data, key, 0, data.length - 1);
}
/**
* Private helper method for binary search that uses recursion.
* @param data, int array to search against (ordered in ascending order)
* @param key, int key value to search for
* @param lowerBound, lower bound index of the array
* @param upperBound, upper bound index of the array
* @return index if found, -1 if not found
*/
private static int find(int[] data, int key, int lowerBound, int upperBound) {
// Base case 1: not found
if (lowerBound > upperBound) {
return -1;
}
int mid = lowerBound + (upperBound - lowerBound) / 2;
// Base case 2: found
if (data[mid] == key) {
return mid;
}
// Recursive cases
if (data[mid] < key) {
return find(data, key, mid + 1, upperBound);
}
return find(data, key, lowerBound, mid - 1);
}